50year male with Diabetes,Renal failure ,Papular lesions with koebner Phenomenon
CHIEF COMPLAINTS
50 year male farmer by occupation came with complaint of
Itching in the front and back and both upper arms(since 2 months)
Nausea,loss of appetite(since 7days)
Decreased urine output(since 1day)
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS
He started his career at the age of 13years(1986) as lorry cleaner who used to accompany with driver for the first 2years.At his 15years age started driving the lorry by himself.
Till 45years(2019) he continued the same profession.He used to drive 100km to and fro in a day.Depending on his requirement of money he used to work 4-6 days in a week.
5 years back as he was getting tired easily(not able to drive long distance)went to local hospital, diagnosed as having high sugars started on OHA.He stopped driving as it is more stressful and started farming his 3 acre land.
He used OHA for 1year,later swithed to insulin as sugars were not in control.From 4years he is on inadequate dose of insulin.He used to take insulin dose (16U/18U) once in a day(against to twice a day dose prescribed by doctor) bcz whenever taking twice a day, intermittently he was having hypoglycaemic symptoms like sweating, palpitations,weakness.
2years back he had trauma(thorn prick) to left second toe, it got worsened after getting treatment for 15day by local rmp.Came to our hospital,disarticulation of left second toe was done.
From one year patient is having on and off pitting type of pedal edema till knee.No history of any associated orthopnea/PND
2months back he had itching at the back more at night.Itchy lesions gradually spread from back to front, buttocks,upper arms.
From 7days patient is having symptoms of nausea, loss of appetite.From 1day he was having decreased urine output, came to our hospital for further management.
No history any fever,orthopnea,PND,dyspnea
PAST HISTORY
k/c/o DM2 - 5years back(1year-used OHA,from 4years he was on insulin once daily)
No history of Hypertension,asthma,TB,epilepsy,thyroid disorders
In October 2022,patient had complaint of both lower limb and upper limb weakness(not able to get up from bed),he was diagnosed as hypokalemic paralysis(sr k -1.7meq/l),with potassium correction he regained his power in the lower limbs and upper limbs.He used syp potcklor for 1week.No similar episodes subsequently
PERSONAL HISTORY
He wakes up at 7:00am in the morning,go his his farm, water his field and comes back at 10:00am eats tiffin.At 11:00am he goes back to farm and till 6:00pm he works there.Take insulin in the afternoon before eating lunch.After coming home, he bathe and eat food at 8:00pm and sleep's by 9:00pm
He had two 2daughters.All are married and having children.
Addictions : he eats umber,drinks alcohol during occasions and family gatherings
FAMILY HISTORY
No similar complaints in the family
MEDICAL HISTORY
He takes inj insulin S/C once daily
GENERAL EXAMINATION
Patient is conscious, coherent,co-operative.Moderately built and Moderately nourished.
Blood pressure-140/80mmhg,right arm, supine position
Pulse-90/min,regular rythm,normal volume.
Respiratory rate-18/min,thoraco abdominal
Temperature-98 F
Spo2-98% on room air
Grbs-420mg/dl
No pallor, icterus,clubbing,cyanosis,lymphedenopathy,edema of legs
No raised JVP
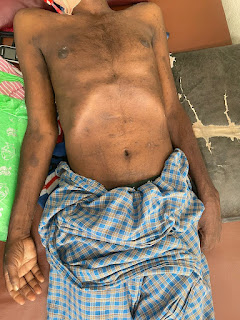
SKIN examination :-
Papules present over back, front,upper arms, buttocks.Koebner phenomenon +.
Hyperpigmented patches diffusely present on back front and over upper arms.Right foot plantar keratosis present.
Left foot second toe is absent
SYSTEMIC EXAMINATION
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM :
Higher mental functions
-Patient is conscious, coherent,co-operative.Oriented to time, place,person.
-Speech = Fluency,comprehension,repetition intact
-Memory =Recent,Remote,Immediate : Intact
Cranial nerve examination -
2 - Visual acuity RE-6/60,LE-CF 1mts
other cranial nerves are normal
Motor examination :
Bulk of muscle normal on both sides on inspection
Hand grip 100% on both sides
Tone
Right. Left
Upper limb. Normal. Normal
Lower limb. Normal. Normal
Reflexes
Right. Left
Biceps. - -
Triceps. - -
Supinator. - -
Knee. - -
Ankle. - -
Plantar. flexor flexor
Sensory examination:
1.Spinothalamic: R L
Crude touch + +
Pain + +
2.Posterior column:
Fine touch + +
Vibration Reduced
ankle - - --
Knee. -- --
Wrist. 6sec 6sec
Position sense
LL. Rt-6/10. Lt --5/10
3.Cortical
Stereognosis: + +
Graphesthesia +. +
CEREBELLUM:
Finger nose and finger finger test were normal
No dyadiadokokinesia
No pendular knee jerk
Heel knee test : normal
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM :
-Elliptical & bilaterally symmetrical chest
-No visible pulsations/engorged veins on the chest
-Apex beat seen in 5th intercostal space medial to mid clavicular line
-S1 S2 heard
-No murmurs
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Upper respiratory tract normal
Lower respiratory tract :
-Trachea is central
-Movements are equal on both sides
-On percussion resonant on all areas
-Bilateral air entry equal
-Normal vesicular breath sounds heard
-No added sounds
-Vocal resonance equal on both sides in all areas
PER ABDOMEN :
-Scaphoid
-No visible pulsations/engorged veins/sinuses
-Soft,non tender, no guarding and rigidity, no organomegaly
-Bowel sounds heard
PROVISIONAL DIAGNOSIS
Uremic symptoms(secondary to CKD)
Papular lesions on upper trunk, back,buttocks and upper arms with Koebner phenomenon
?Diabetic neuropathy
With H/0 hypokalemic paralyses(in oct 2022)
k/c/o DM2(Since 5years)
-----------------------------------
INVESTIGATIONS
In oct 2022,when he had the episode of hypokalemic paralysis
In our hospital on 22-4-2023
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
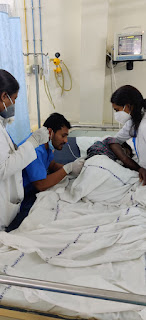
AKI ON CKD(Initiated dialysis on 23-4-2023)
Papular lesions with koebner phenomenon(?Lichen planus ?Lichenoid drug eruption ?Uremic pruritis)
History of Hypokalemic paralysis in oct 2022(sr K+ =1.7meq/l)
Left foot second toe disarticulated in 2021(secondary to trauma-thorn prick)
?Diabetic Neuropathy
k/c/o DM2(since 5years)
-----------------------------------------------------
Indication of dialysis in this patient =Anuria with Uremic symptoms(nausea, loss of appetite)
After dialysis(On 23-4-2023) patient symptoms improved
Post dialysis RFT
------------------------------------------------
Pathophysiology of Hyperglycemia and Renal Failure
Generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) induced by hyperglycemia
Increased stimulation of glucose oxidation pathways in non-insulin-dependent cells leads to the activation of alternative pathways, increased production of RONS and oxidative stress (OS) in hyperglycemic state.
Glucose auto oxidation
In glycemic homeostasis and in the absence of oxygen, glycolysis is the primary energy source in the cells.
The synthesis of substrates by glycolysis activates two other energy pathways: the tricarboxylic acid cycle (or the Krebs cycle) and the electron transport chain (ETC) (or the oxidative phosphorylation) in the mitochondria through protein complexes
In DM, the hyperglycemic state promotes the overactivation of the three main energy pathways previously described. The increased stimulation of glycolysis and Krebs cycle result in elevated production of reduced flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), fed into the ETC.
The ETC is a source of reactive oxygen species (ROS), especially in renal cells, which have a large number of mitochondria
Ros which are harmful to mitochondrial DNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibiting the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). These changes alter the activation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), and thereby affect mitochondrial biogenesis, by increasing mitochondrial fission and the synthesis of defective mitochondria
This can lead to impairment of the ECT functions, with reduced synthesis of ATP, leading to renal cell lesion and apoptosis
In addition, increased glycolysis causes hyperactivation of polyol and hexosamine metabolic pathways, and increases the synthesis of AGEs and activation of PKC. This also result in decreased ATP levels, contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction and fragmentation
Schematic representation of the pathways preceding glycolysis and induction of oxidative stress. ETC: electron transport chain; 1,3-BPG: bisphosphoglycerate; G6P: glucose 6-phosphate; G3P: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; F6P: fructose-6-phosphate; F-1,6-P: fructose-1,6-phosphate; PKC: protein kinase C; AGE; advanced glycation end-products























Comments
Post a Comment